Node - Calculation
Node Overview
The Calculation node is a data processing step within a workflow. It receives input data and performs specific operations to generate results for downstream nodes.
This node does not modify original field values; instead, it produces new computed values that can be used in subsequent nodes.
How It Differs from Formula Fields in Worksheets
-
Cross-record & cross-worksheet operations:
The Calculation node supports referencing fields across different worksheets or multiple records. In contrast, formula fields in a worksheet can only access fields within the same worksheet.
-
Timing of execution:
- Calculation nodes are triggered after a record is saved and the workflow is executed.
- Formula fields calculate values immediately during record editing and display them in real-time.
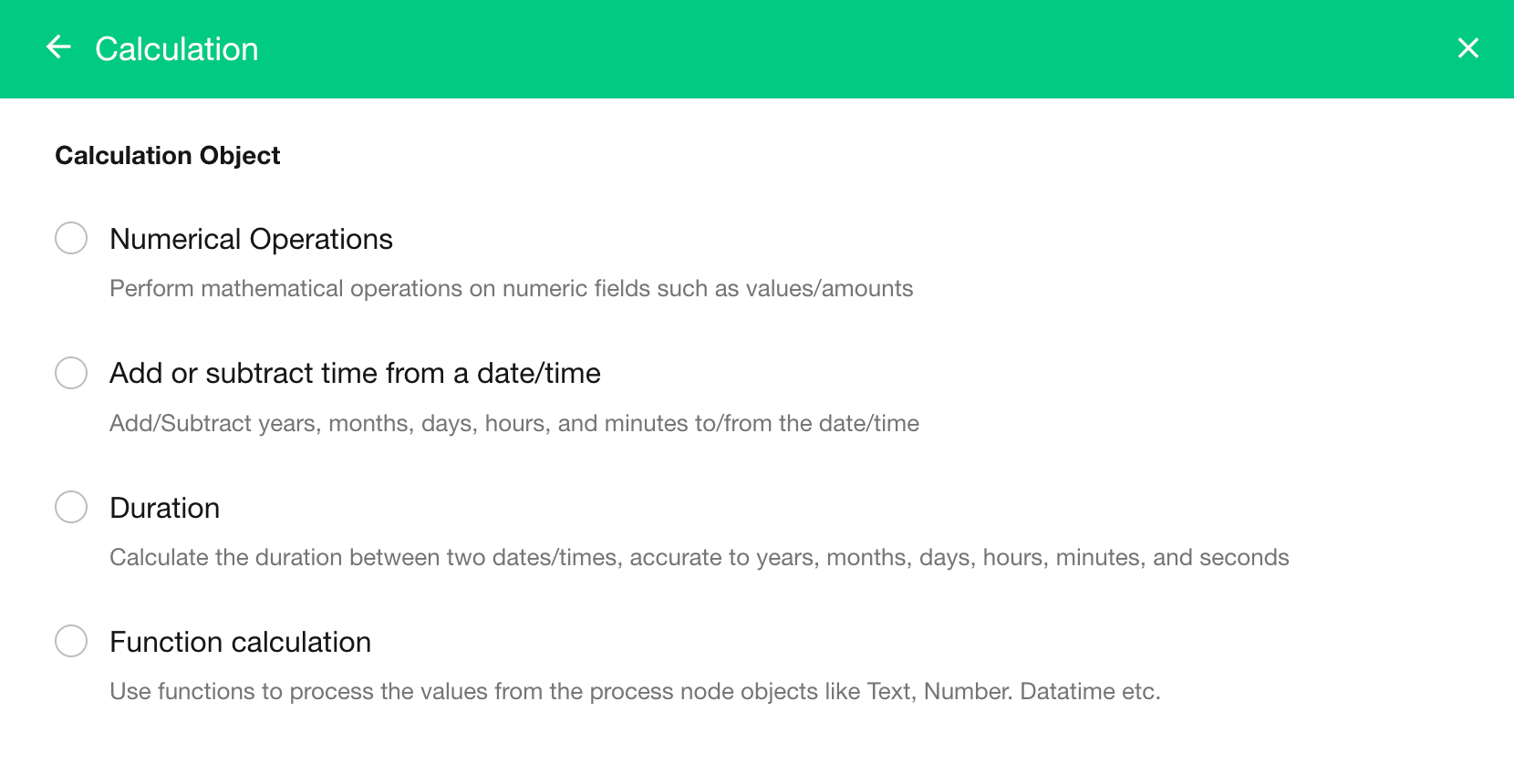
Supported Calculation Types
-
Arithmetic operations between number or currency fields
-
Duration calculation between two date fields
-
Date adjustment: add or subtract time from a date to compute a new date
-
Data processing using functions
How Calculation Results Are Stored
-
Static Calculation
The result is calculated and saved when the workflow reaches the Calculation node. Once saved, the result will not change even if the source field values are updated later.
-
Dynamic Calculation
The result is not immediately calculated when reaching the Calculation node. Instead, it is calculated on demand when referenced by a downstream node. If the source field values change, different downstream nodes may receive different results.

1. Numeric and Currency Calculations
This type of calculation is typically used across different records.
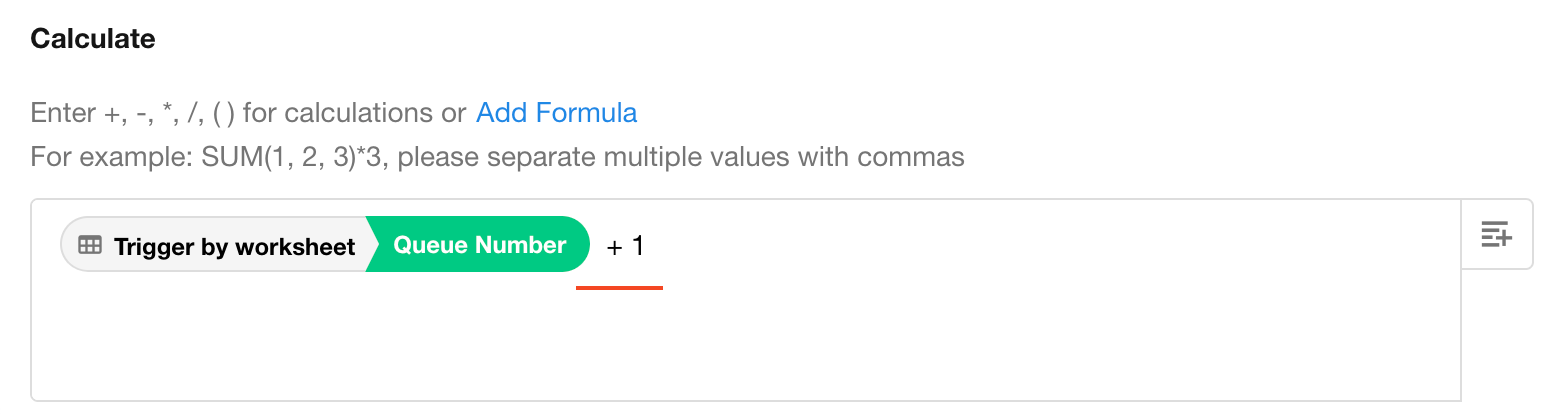
For example, in a restaurant queue management worksheet, when a new queue record is added, the system can query the worksheet and retrieve the current maximum queue number from existing records and calculate max number + 1 to generate the new queue number.
Configure the Calculation Node
1. Add a Calculation Node and Choose Numeric Operation
2. Select Fields for the Calculation
You can select numeric or currency fields from previous nodes in the workflow.
You can also calculate using constants directly.
3. Define the Formula
You can either manually enter a formula using operators (+, -, *, /, ()),
or use a built-in system formula. In this example, both methods work to calculate the next queue number.
-
Custom Formula

-
System Formula
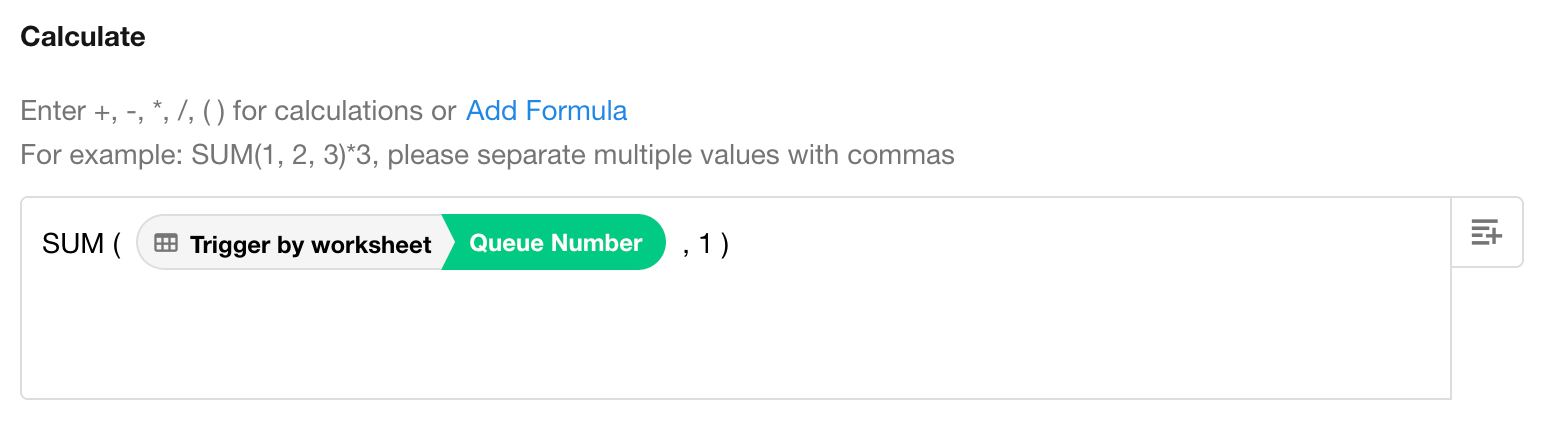
Tips:
-
Decimal results are rounded to 2 decimal places by default.
-
When using system formulas, separate fields inside parentheses with commas (
,); When writing custom formulas, make sure to include valid operators. -
If any field involved in the calculation is deleted, the result will be empty.
4. Treat Empty Fields as Zero
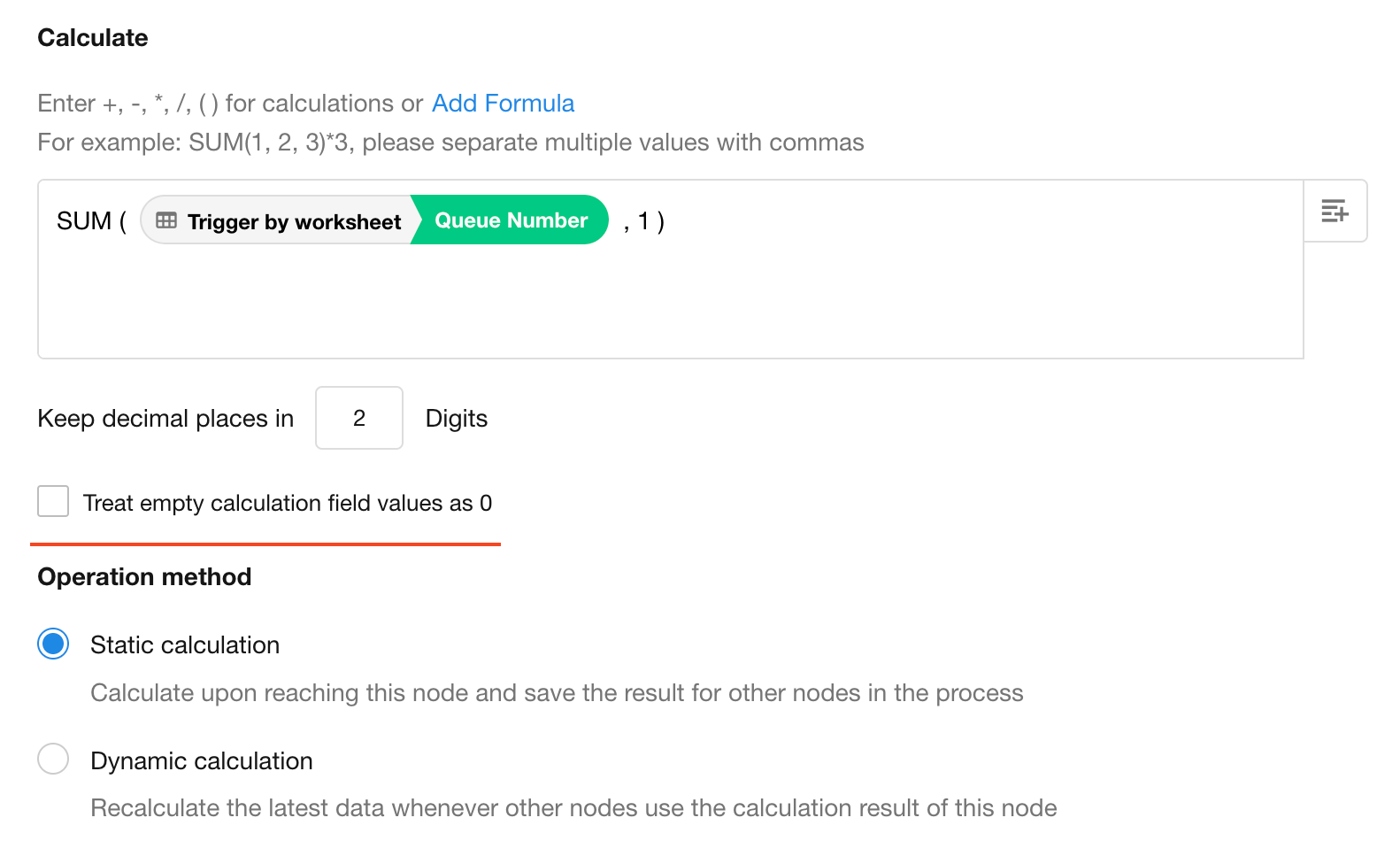
When using a custom formula like Field 1 + Field 2 + Field 3, the result will be empty if any field is empty.
Enable the "Treat empty fields as 0" option to ensure calculations still return valid results.
If the field used as the denominator is empty, the result will always be empty.
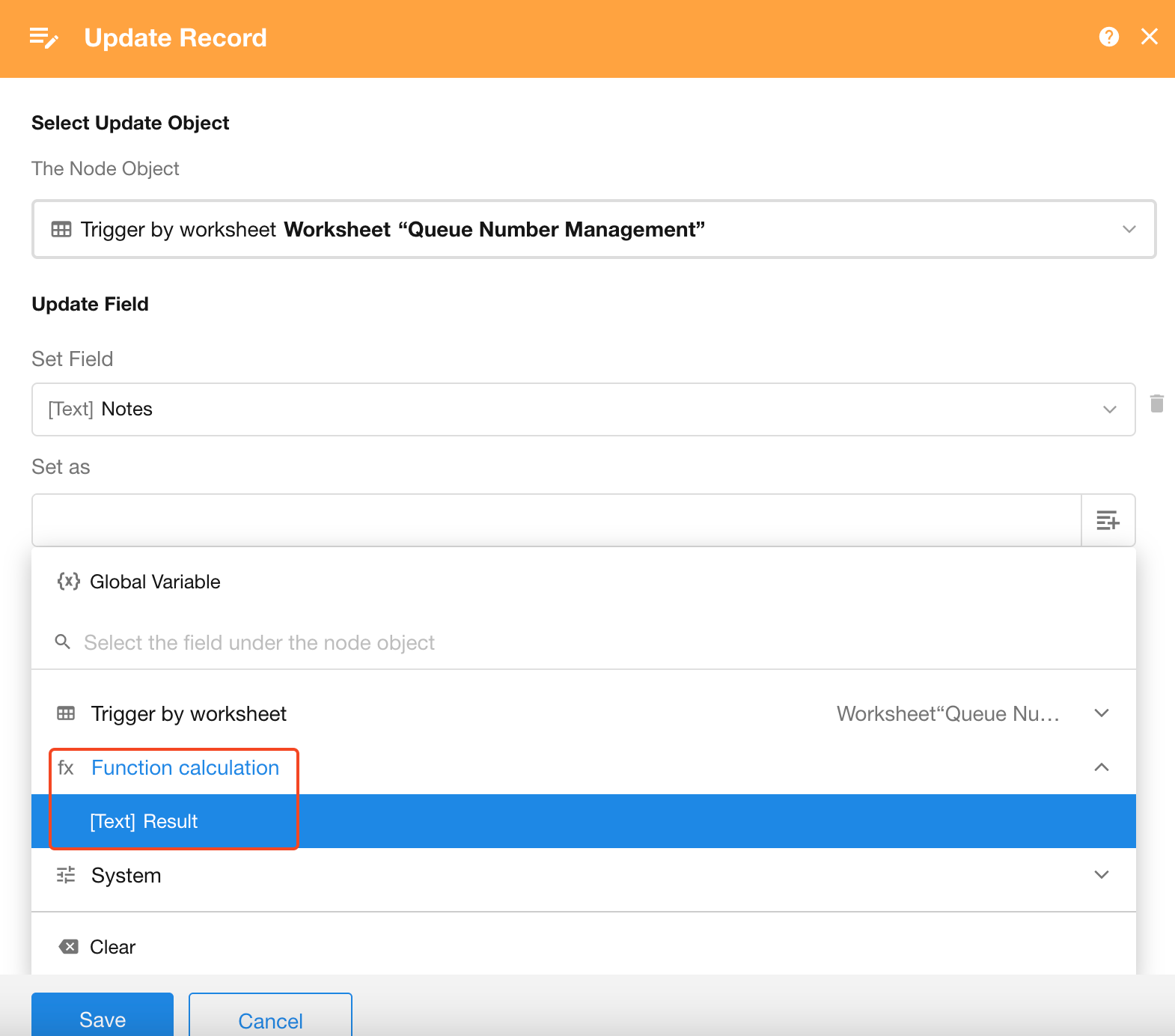
5. Use the Calculation Result in Downstream Nodes
Subsequent nodes can directly reference the result from this calculation node.
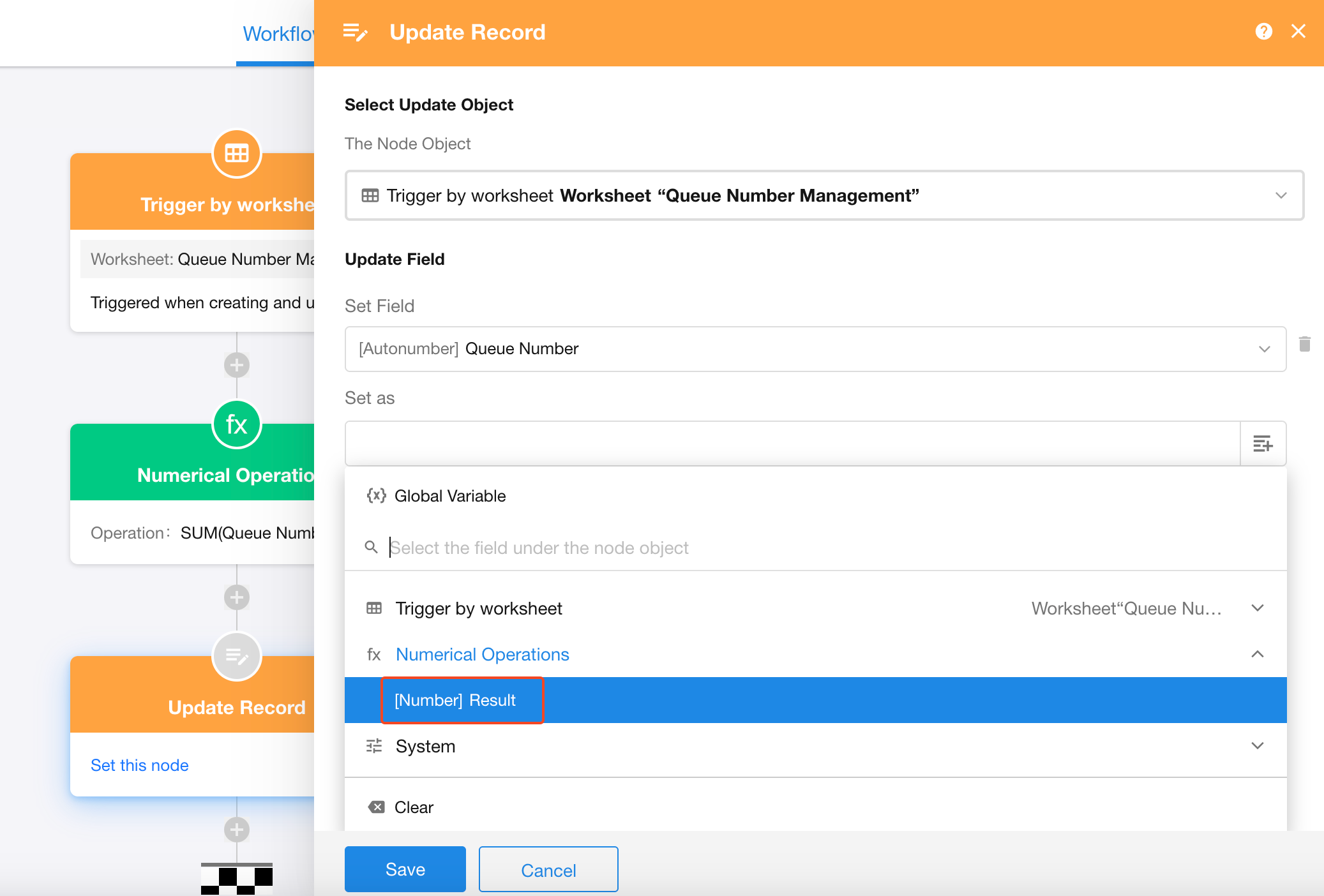
If the result may be empty, consider using a conditional branch to handle different outcomes.
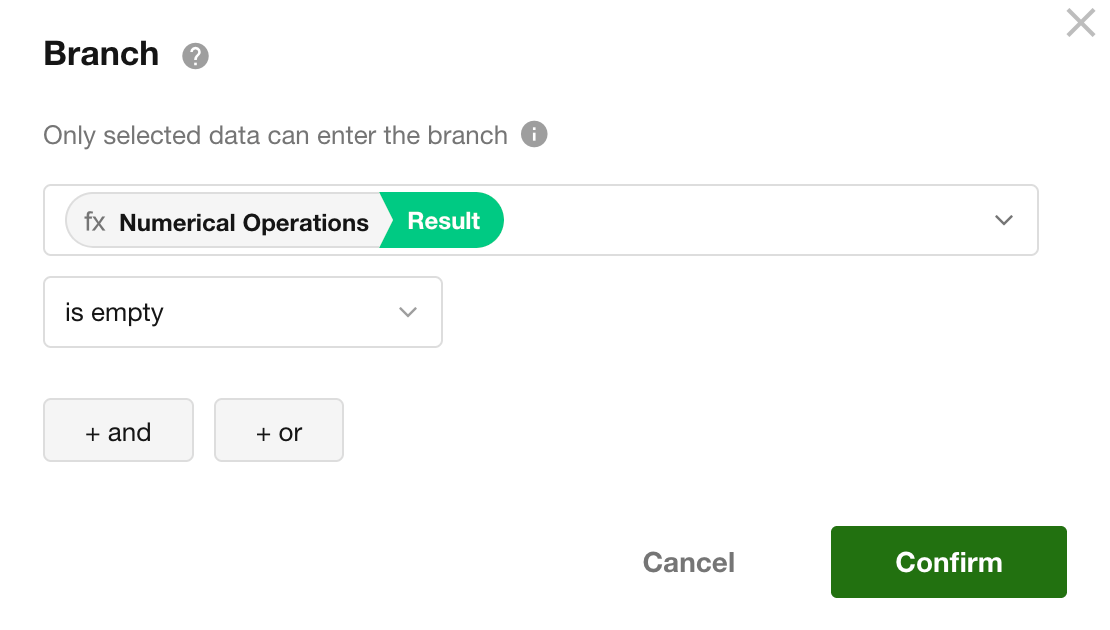
2. Add/Subtract Duration from a Specified Date
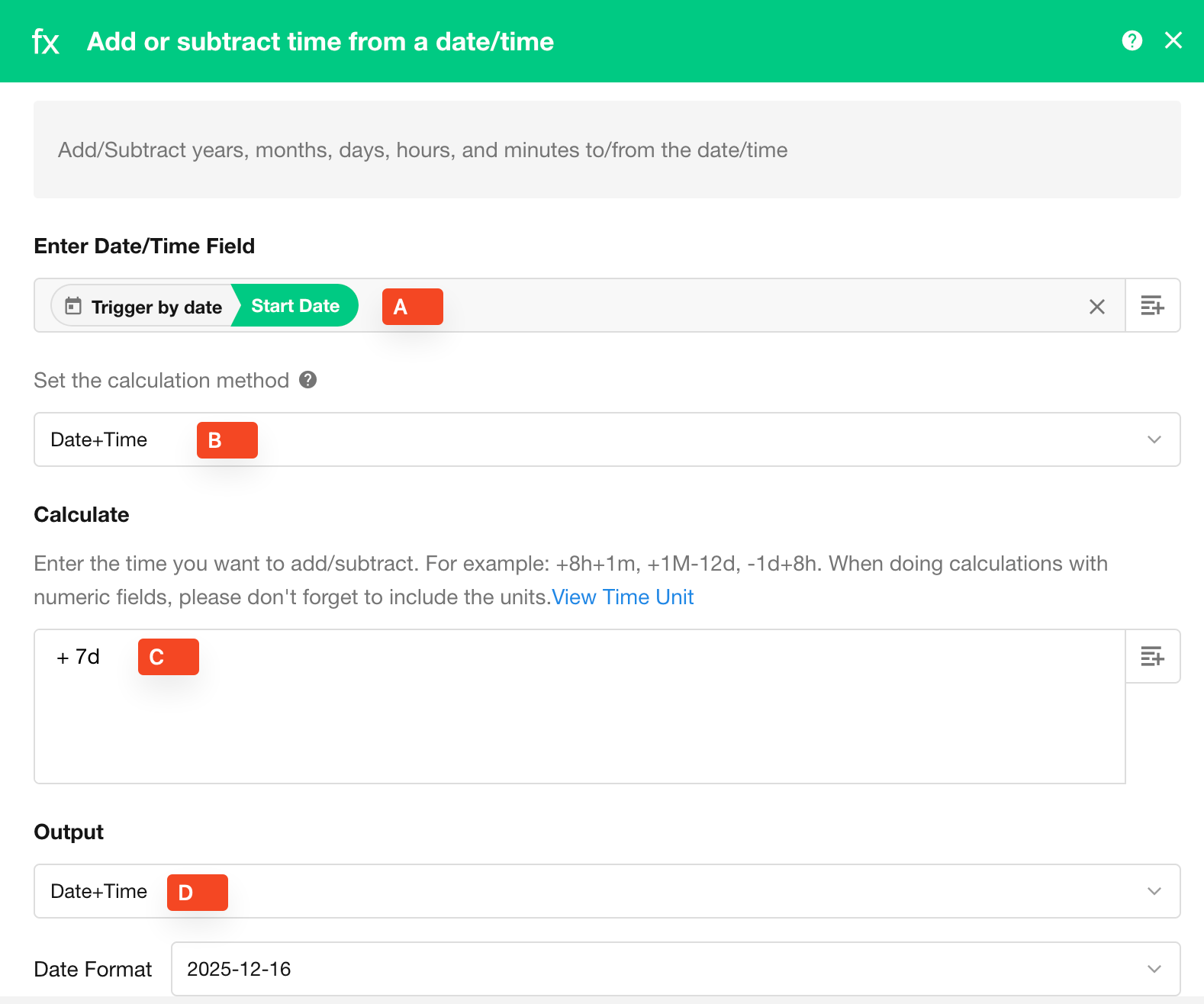
Use this operation to add or subtract a specific duration from a given date field.
-
A: Select the target date field that you want to modify.
-
B: Choose the calculation format:
-
Date: Only the date part is used (e.g.,
2021-11-11 12:50is interpreted as2021-11-11 00:00) -
Date + Time: The full timestamp is used (e.g.,
2021-11-11 12:50is interpreted as2021-11-11 12:50)
-
-
C: Define the formula. In the example above, the result will be the original date plus 7 days.
-
D: Choose the output format for the calculated result.
Tips
-
The formula must start with an operator (
+or-). -
Units:
Y= YearM= Monthd= Dayh= Hourm= Minute
Mandmare case-sensitive.
-
Each number must be preceded by an operator and followed by a unit.
For example:+8h+1mis valid. -
If you're referencing a numeric field from another node, just append the unit directly — no operator or symbol in between.
Example 1: Date Format
- Input:
2020-10-12 13:50 - Format: Date
- Formula:
+7d+3h-2m
The base date becomes 2020-10-12 00:00.
Adding 7 days + 3 hours − 2 minutes gives:
Result: 2020-10-19 02:58
Example 2: Date + Time Format
- Input:
2020-10-12 13:50 - Format: Date + Time
- Formula:
+3h
Result: 2020-10-12 16:50
Example 3: Get 8:00 AM of the Current Day
If the system time when the calculation node executes is 2020-12-21 14:37:
- Format: Date → base becomes
2020-12-21 00:00 - Formula:
+8h - Result:
2020-12-21 08:00
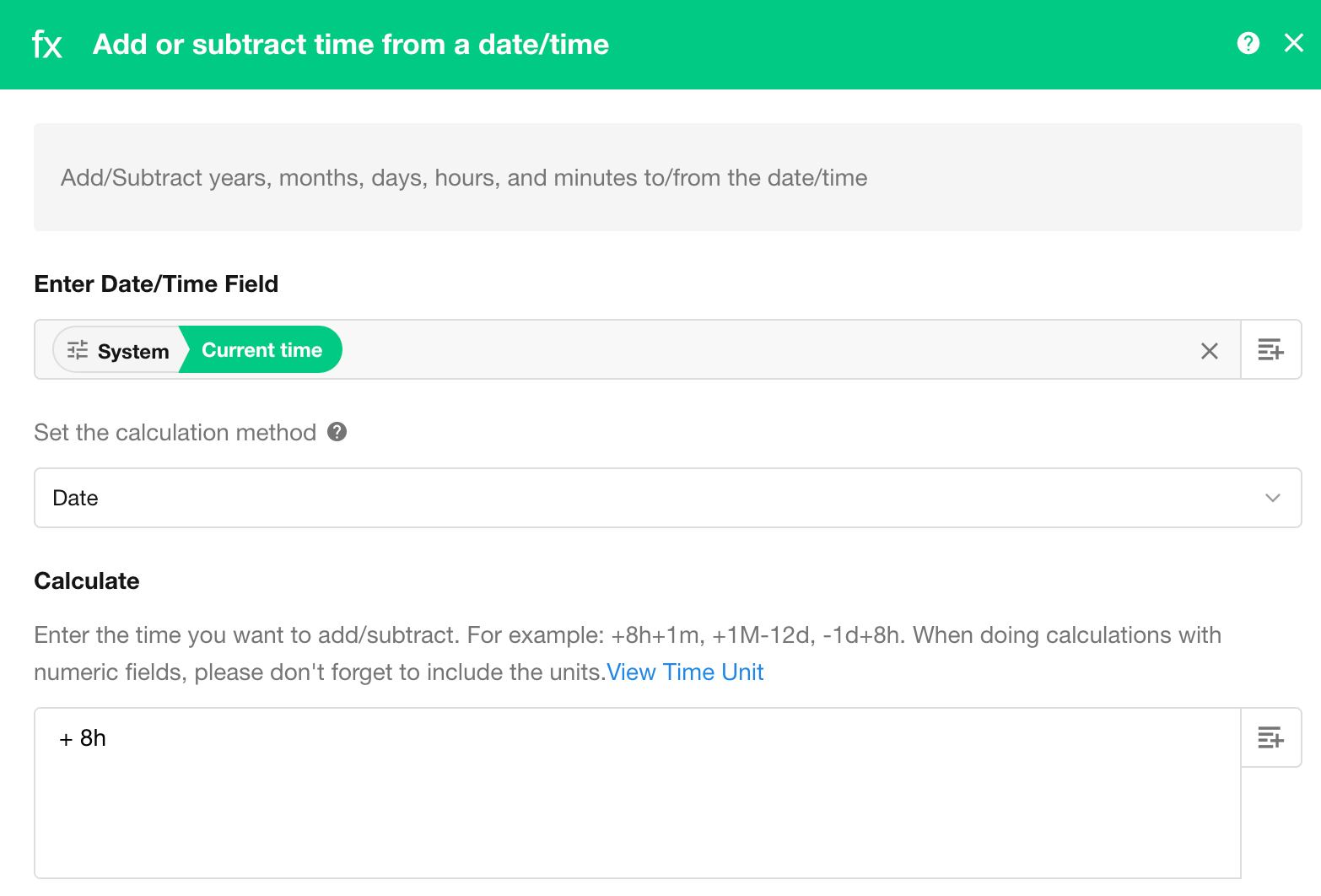
3. Calculate Duration Between Two Dates
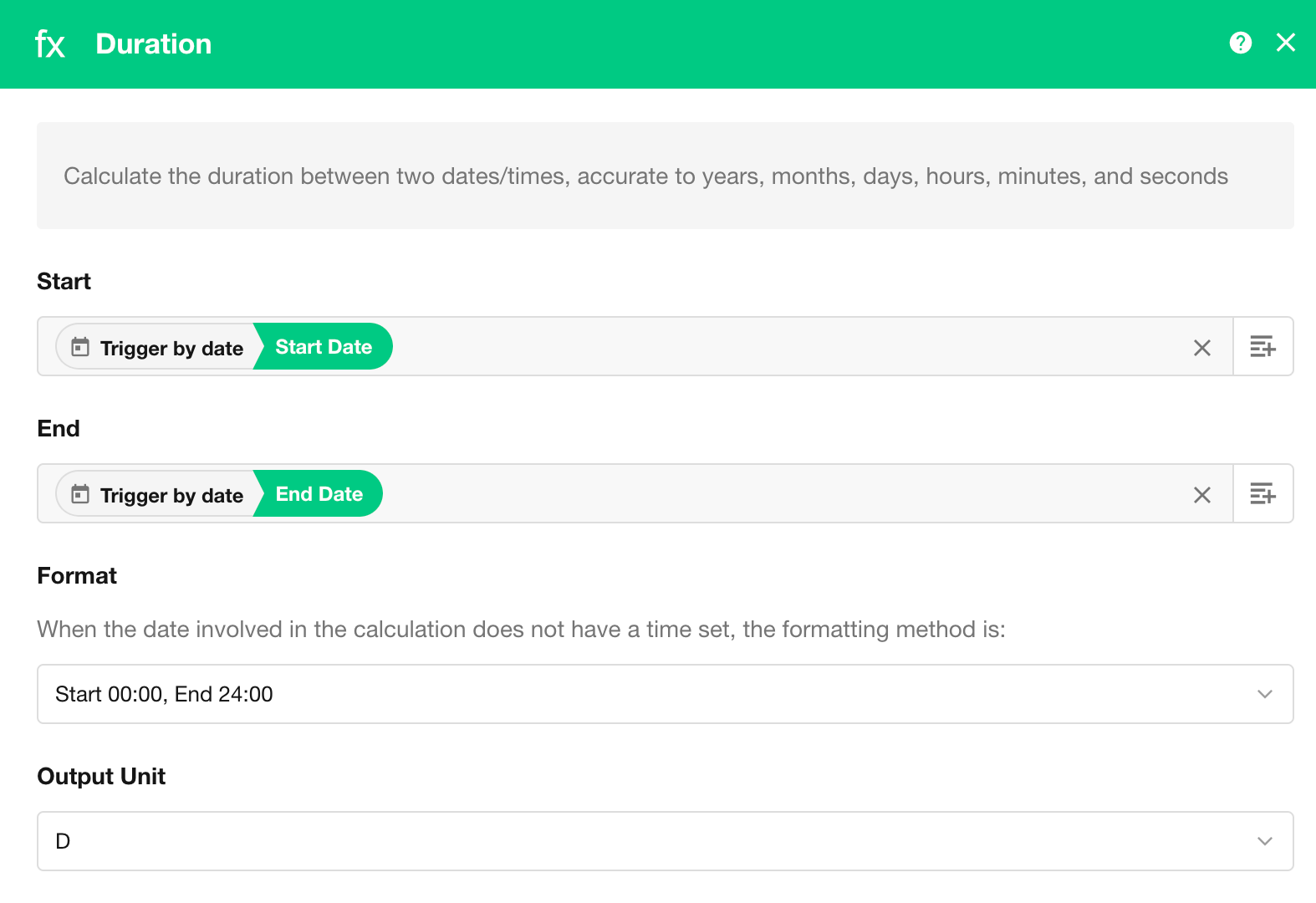
This function works similarly to using a formula control in a worksheet to calculate the duration between two dates. You specify the start date and end date fields, then define the format to be used in the duration calculation.
- Format 1: Start at 00:00, End at 24:00
- Format 2: Start at 00:00, End at 00:00
If the selected fields are date-only (without time), a default time will be appended as per the format selected. If the fields already contain timestamps, the calculation uses the actual datetime values.
Example 1
-
Start Date:
2020-12-13 -
End Date:
2020-12-14 -
Output Unit: Days
-
Using Format 1:
- Start:
2020-12-13 00:00 - End:
2020-12-14 24:00 - Result: 2 days
- Start:
-
Using Format 2:
- Start:
2020-12-13 00:00 - End:
2020-12-14 00:00 - Result: 1 day
- Start:
Example 2
- Start Date:
2020-12-13 - End Date:
2020-12-14 12:00 - Output Unit: Hours
Since the end date includes a time component, both Format 1 and Format 2 produce the same result:
- Start:
2020-12-13 00:00 - End:
2020-12-14 12:00 - Result: 36 hours
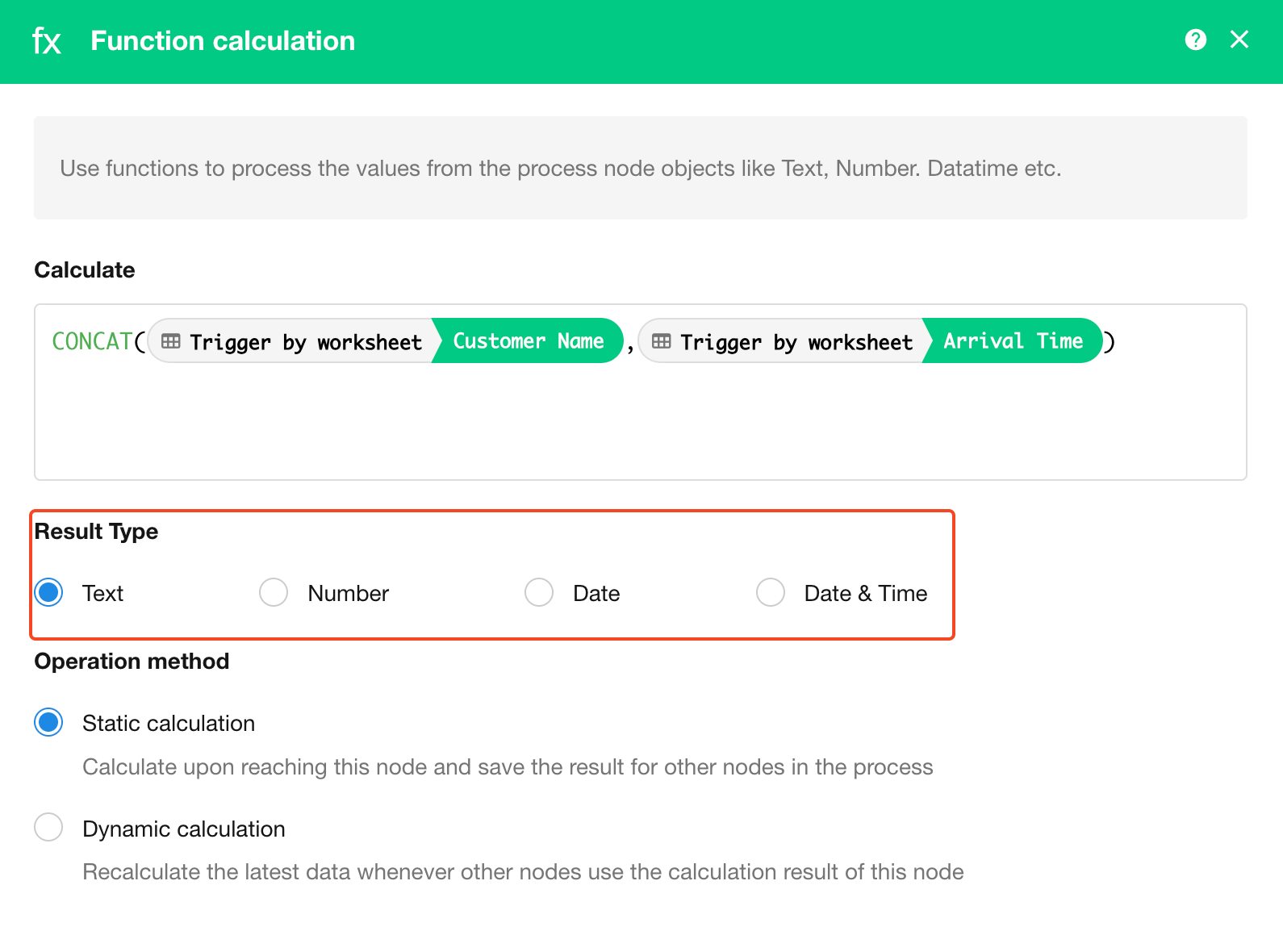
4. Function Calculation
Using functions, you can process the values of node objects such as text, numbers, or dates and return results in the desired format. Common examples include:
- Using the
YEAR()function to extract the year from a date. - Using the
REPLACE()function to remove the+86prefix from a phone number. - Using the
DISTANCE()function to calculate the distance between two location fields.
Configure the Calculation Node
1. Add a calculation node and select the "Function" option
2. Define the function formula
For a full list of supported functions, see Learn more about functions
3. Select the output data type for the calculation result
4. Use the result in subsequent workflow nodes
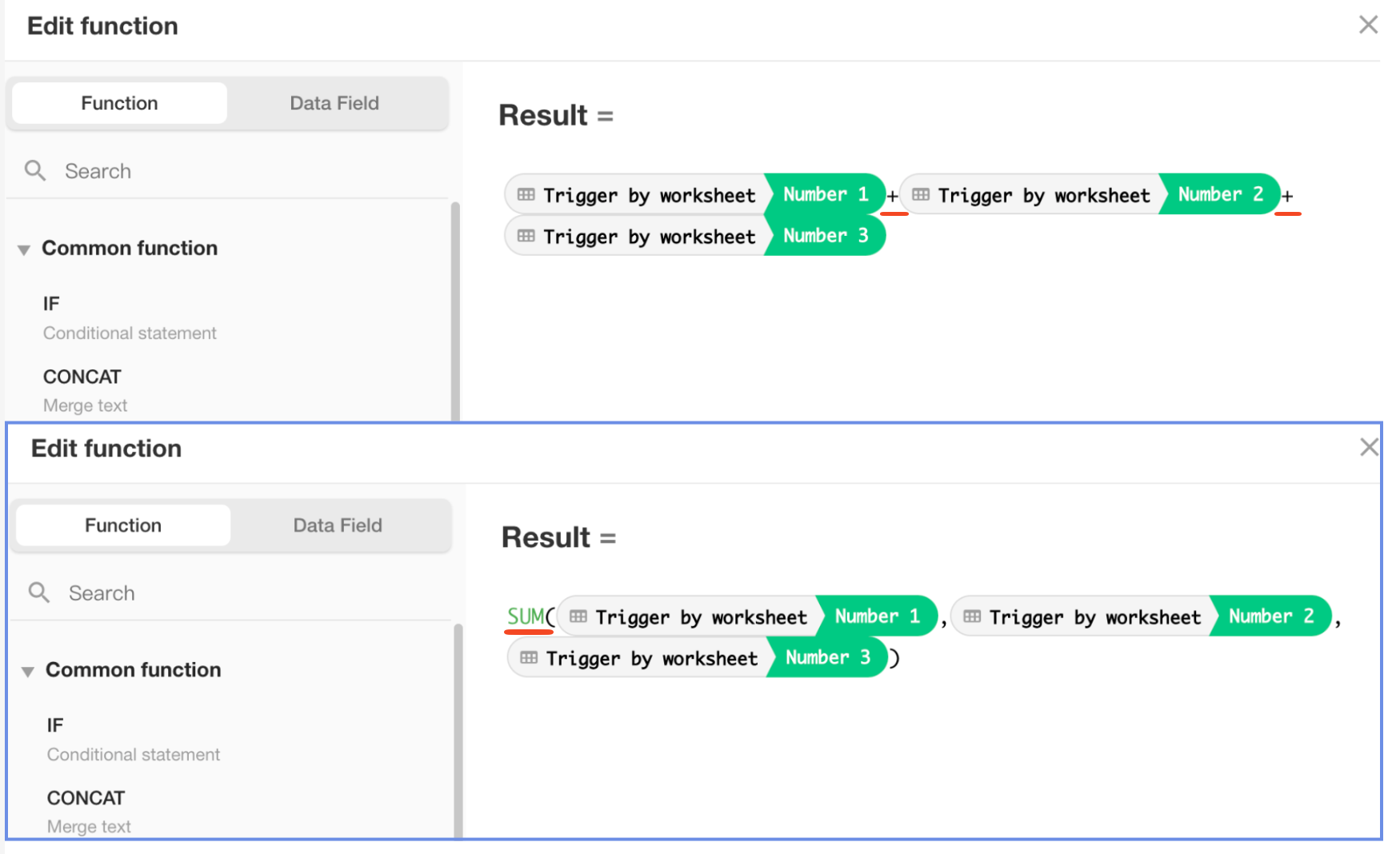
Tips
- In addition to using functions, you can define custom calculation rules. For example, to concatenate two fields, use
+.
However, when using custom logic, if any referenced field is deleted or empty, the result will be empty. To avoid this, use built-in functions where empty values are treated as0by default.
- If the result of a function cannot be converted to the selected output type, the result will be null.
For example, if the result of1 + 1is2, but the output type is set to Date, the result will be empty.